The world seemed to be a small place after satellites empowered the telecommunication systems because it has allowed people across the globe to connect and join roundtable sessions even when they are not physically close to each other. These radio-based satellite systems are hovering above the geostationary orbit (the orbit above the equator) to ensure that communities are provided with fantastic telecommunication that benefits different aspects, like:
- Allowing distance insensitive visualisation of earth points that have location restrictions when analysed physically
- Allowing reliable communication systems
- Building early warning systems of incoming perils or conflicts like ballistic missiles and offering disaster recovery information
- Empowering the television networks
- Enable comprehensive visualisation for space projects
- Single-hop transmission services
- Tremendous visualisation and updates for aviation specialists
- Weather forecasting services
Today in Cerexio Blog Archives, we are elaborating on how satellite technology optimised the telecommunication field and what are the benefits that satellite technology has enabled for telecommunication industry experts around the world.
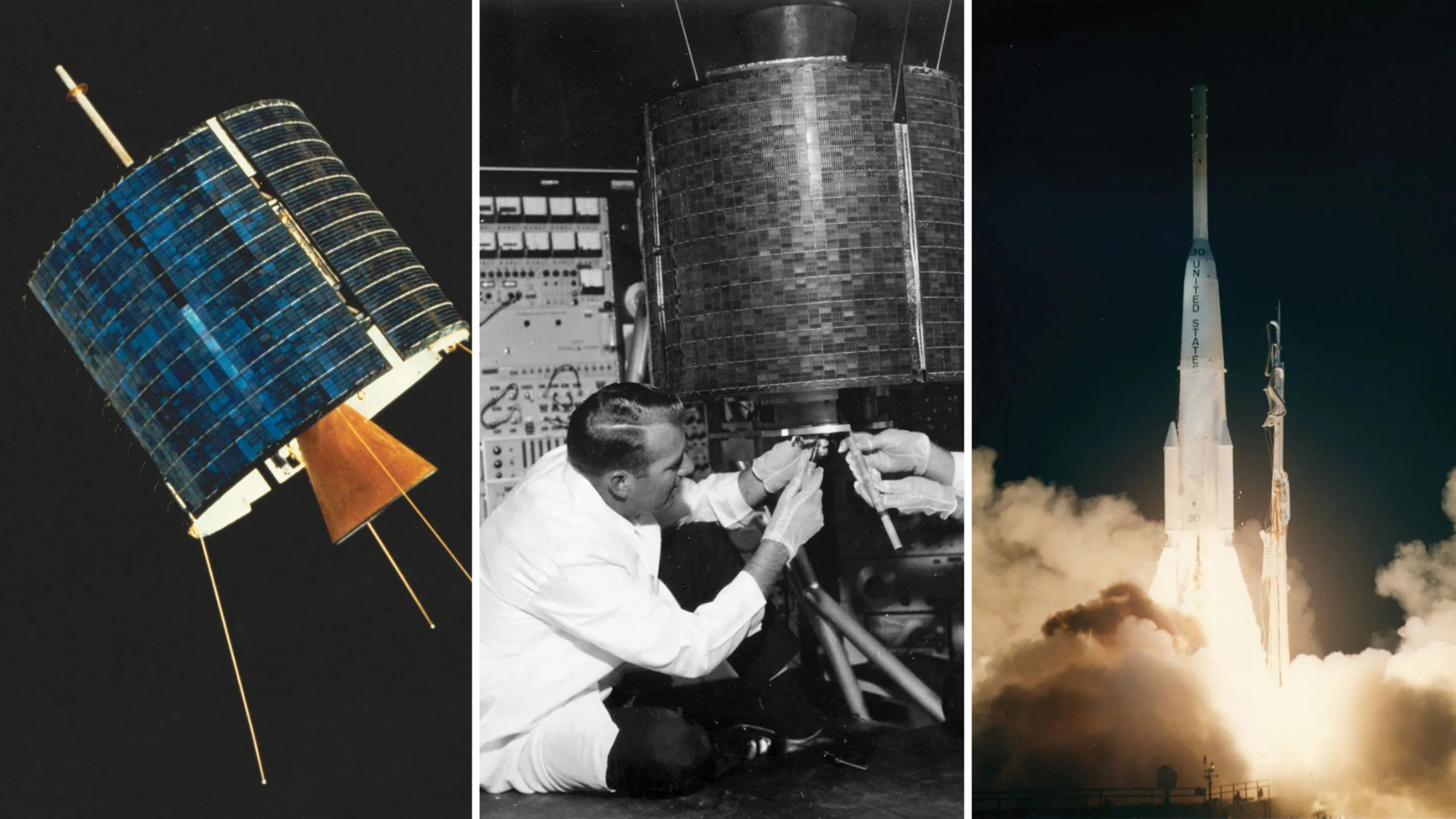
INTELSAT I- The First Commercial Satellite Launched for Telecommunication Purposes
INTELSAT 1 was a cylindrical-shaped satellite with a 684-mm height and 710-mm diameter. It weighed 38.6 KG and was operated by COMSAT and International Telecommunications Satellite Consortium. This satellite helped the telecasting of a live spacecraft splashdown in 1965, benchmarking the beginning of the evolution of telecommunication in the US and Europe. The INTELSAT I was also used to predict world maps too. This satellite was deactivated in August 1969. This satellite was a breakthrough in the space physics and telecommunication industries.
Types of Satellite Technologies for Telecommunication
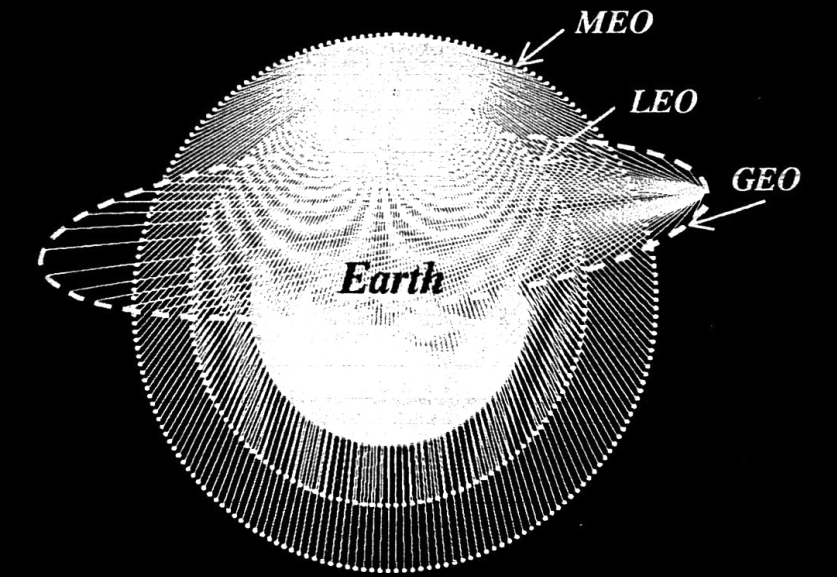
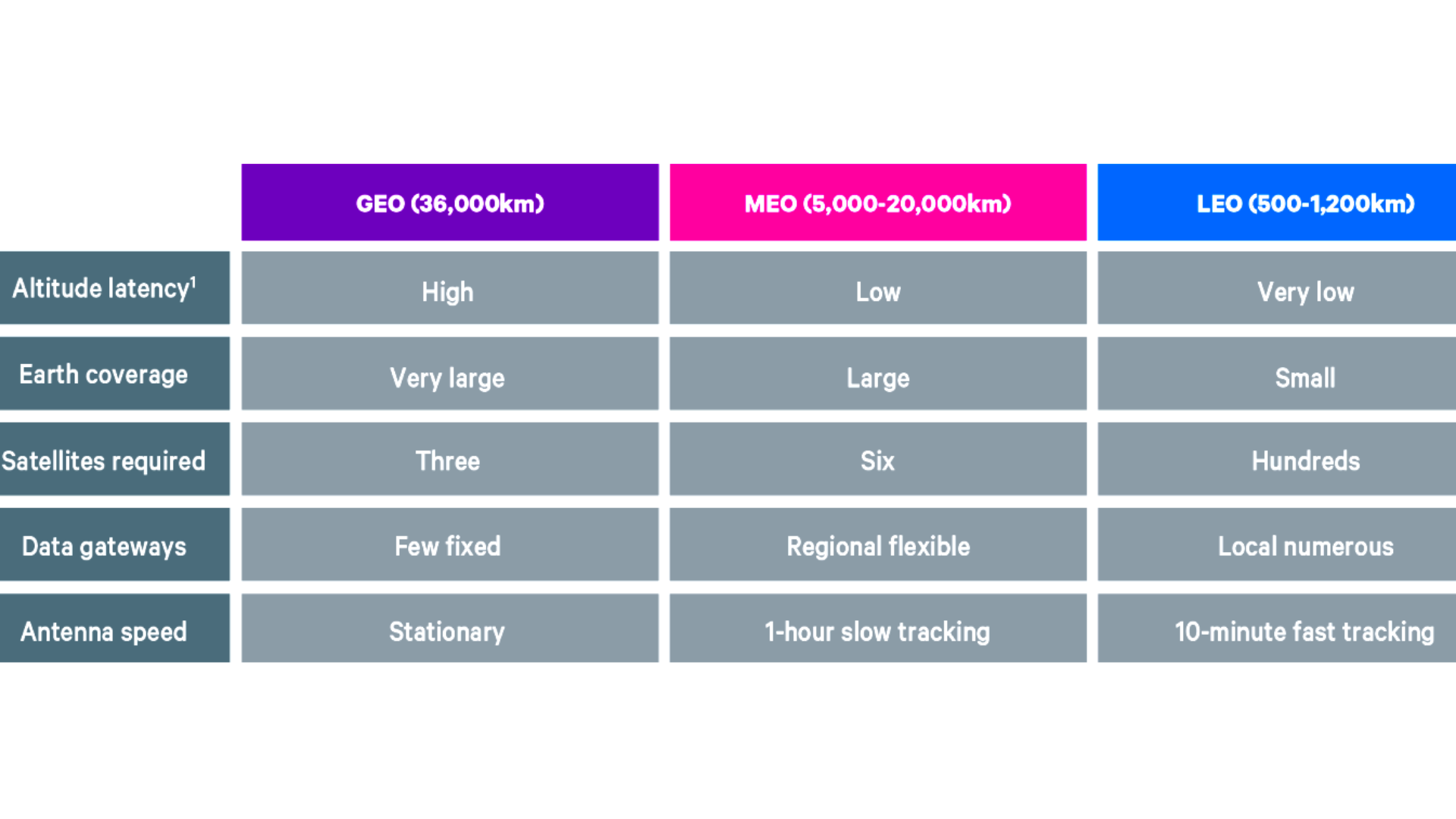
Geostationary Earth Orbit Satellite (GEO)
Description: It is a geostationary satellite (moves at the same speed as the Earth), and a few GEO satellites are sufficient to scan the entire world. It can have a propagation delay of 250 ms. GEO satellites are not efficient in powering the internet, handling small transactions because of this delay.
Example: ACTS (Advanced Communication Technology Satellite) is a GEO launched by NASA in 1993, which was inherited with the propensity to transmit information at a speed of hundreds of MB/sec.
Uses: For both non-interactive telecommunication (Video on Demand, Asymmetric Data services and TV Broadcasting) and interactive telecommunication (voice, video conferencing and other multimedia services)
Medium Earth Orbit Satellite (MEO)
Location: 6250 to 13,000 miles away from the globe
Description: MEO satellites are not geostationary like GEO, and they have a time delay of ¼ to ⅙ that of GEO delays- so they are faster than GEO. Multiple MEO satellites will be required to cover the whole earth- however, the number of satellites for earth coverage is more than GEO technology and less than LEO technology. Latency and courage capabilities of MEO satellites are second to LEO satellites.
Example: GLONASS Galileo (Altitude of 23,222 kilometres), (Altitude of 19,100 kilometres) and GPS (Altitude of 20,200 kilometres)
Uses: Voice communication, GPS tracking, and other navigational applications. Useful for commercial enterprises, agencies, service providers and government or state establishments related to cruise, aero, network backhaul commercial maritime humanitarian relief operations.
Low Earth Orbit Satellite (LEO)
Description: LEO satellites have a 0.03-second time delay during transmission- it allows hyperspeed connectivity for telecommunication systems making it more efficient and effective for faster communication systems. These satellites must have a vast number to cover the whole earth, and setting up the LEO satellite system is a costly investment. However, companies who have invested in LEO satellites end up targeting and winning in profitable marketing segments like enterprise broadband and internet mass-consumer.
Example: Hubble Space Telescope, Military Observation Satellites, Spot Family of Satellites (For Earth Imaging and Survey Purposes)
Starlink –engineered by SpaceX- is one of the handiest technology devices that use advanced technologies of low-orbit satellites. It uses the satellite data to enable faster internet (with latency rates as low as 20ms), better coverage and 100 Mb/s and 200 Mb/s download speeds. This technology helps rural communities to get the luxury of interconnectivity and boost all their industrial sectors including healthcare, education, public services and more.
Uses: Ideal for interactive and responsive multimedia services and delivery of time-sensitive information. They are also used for database access, emailing, breaking news broadcasting, distance learning, direct-to-home videos, newsgathering, e-transactions and many more. It is important to note that this technology is used for remote sensing, addressing scientific discoveries and other new-age technological advancements that are showing remarkable innovations and breakthroughs in the commercial and industrial worlds.
Satellites Application of Satellites in The Telecommunication Industry
- Aeronautical Mobile Satellite Service (AMSS)
- Aeronautical Radionavigation Satellite Service (ARSS)
- Amateur Satellite Service (ASS)
- Broadcast Satellite Service (BSS) (also known as Direct Broadcast
- Broadcast Satellite Service for Radio (BSSR)
- Earth Exploration Satellite Service (EESS)
- Fixed Satellite Services (FSS)
- Inter-Satellite Service (ISS) (also known as
- Inter7 Satellite Links (ISL))
- Land Mobile Satellite Service (LMSS)
- Maritime Mobile Satellite Service (MMSS)
- Maritime Radionavigation Satellite Service (MRSS)
- Meteorological Satellite Service (MSS)
- Mobile Satellite Service (MSS)
- Radiodetermination Satellite Service (RDSS)
- Radio Navigation Satellite Service (RNSS)
- Satellite Service (DBS) or small dish television)
- Space Operation Service (SOS)
- Space Research Service (SRS)
Cerexio- The Best Satellite Technology Partner for Telecommunication Giants
Cerexio allows satellite data-based telecommunication service enablers to imagine the future and meet the future in the most cost-effective, faster and efficient manner possible. We are on a journey to allow a truly 5G-driven globally unifying world for the first time by interconnecting telecommunication stakeholders around the world with optimal satellite technologies. Whether you are a telecommunication service provider tackling the network issues of the air, land or sea, Cerexio is competent in arranging all the technological tools, suites and equipment required to drive innovation and enabling truly seamless satellite-powered coverages even in remote areas of the globe.
Connect with Cerexio to learn how our data technology kits are enriched with EO (Earth Observation) data extracted from a multitude of satellites and how our services are unrivalled in the technology market for their excellence and updatedness.
