If you are a person lingering in an industrial business or a student learning about the digitally revolutionising industries, the buzzword ‘Industry 4.0’ is one that you frequently tune in on to. The German industrial revolution took turns with technology to enter the next phase in upgrading their industrial networks, hence introducing ‘Industrie 4.0’-German Industry 4.0- to the world which soared around the globe with an influential ripple effect. Now, many countries like Canada, Japan, Australia, Switzerland, Singapore, and Austria have used technologies in the industrial revolution 4.0 to automate their industries and naturally convert their factories into ‘Smart Factories’. So, what are these technologies that are not enhancing but completely transforming everything from businesses to cities to nations?
Technology in Today’s World
Before we address the main topic directly let us be familiar with our version of understanding how we are influenced by revolution 4.0. Compared to a decade or less back in our lives with our lives today, have we not had a drastic change? The way we buy products to the way we travel using apps, even the way we interact with people or play a game when we are bored. In the same way, technology has made our lives different, the stance that business is in is also undergoing vast transformations because of technology. The pressure that is on industries to reduce time on studying the market and being highly responsive to their customers is above the red line. The demand by the market for better everything has never been so vigorous, better efficiency, better flexibility, better quality, and better more. With this compelling force, businesses know that if they fail to satisfy a customer, someone else is going to do it in an instant. This is where the need for Industry 4.0 technologies come hand in hand to support business in adopting unique portfolios in discrete industries to use the palpable futuristic technologies to keep their competitors at bay. This is why having a comprehensive understanding of Industry 4.0 is a vital skill to sustain in a world shrouded with technological efficacies.
This article is about ‘Industry 4.0’ for dummies who intend to explore the new world created by Industry 4.0 in the global industrial realm.
The Evolution of Industries
How is Industry 4.0 any different from the prior Industrial revolutions? If we take a glance back to the previous Industrial Revolutions:
First Industrial Revolution (Industry 1.0)
Mechanisation with steam power. The advent of steam-powered engines, machines, and factories. New manufacturing processes came into play with metallurgy, mining, and other mechanic tools.
Second Industrial Revolution (Industry 2.0)
Electrification empowered mass production, engines, and supercharge product lines to connect markets around the world via globalisation. There was an evident advancement in telegraph, gas, and water supply systems.
Third Industrial Revolution (Industry 3.0)
The development of computers and the internet introduced digital networking to manufacturing industries. Automation is unlocked by digitising networks, machines. Factory robots were used in the industries to carry out tasks in a routine.
Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0)
The convergence of IT systems with the physical systems. Automation enhanced while diminishing the need for human intervention in processes that are done by automated robots. Ample amounts of data are generated to supersede all Industry 3.0 technologies by fostering analytical abilities, predictive, and machine learning capabilities. Ubiquitous cloud computing, additive manufacturing, the Internet of Things, Advanced Robots, Virtual and Augmented Realities are a few of the technologies that made this industrial revolution undergo a revolutionary phase.
Cyber-Physical Systems – the basis of Industry 4.0
So where does industry 4.0 draws its line to distinguish its practices from the Third Industrial Revolution? The best word to explain the disparity would be ‘smart’. Smart machines, to smart houses/businesses, to smart cities to smart nations. Smart machines, or technically termed as ‘Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)’ came into existence during this era. Cyber-Physical Systems are an integration of physics and logic to interact with all sorts of components-digital to analogue, physical to virtual- to provide a foundation for business from any diverse industry to foster Industry 4.0 technologies. It is the basis for Industry 4.0 that bridges the physical world to the digital 4.0 world where the ‘centralised industrial control systems’ became an apex where smart processes and smart products define automation and smart decisions making at every step in Smart Factories. Compared to computers in Industry 3.0, computers today are more connected and have extravagant communication capabilities with each other. They have evolved in Industry 4.0 to make decisions without human intervention. Given below is an illustration that was developed by a group of people that made revisions and graphically represented the raw taxonomy represented by S. Shyam Sunder in a Cyber-Physical System Workshop hosted by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2012.
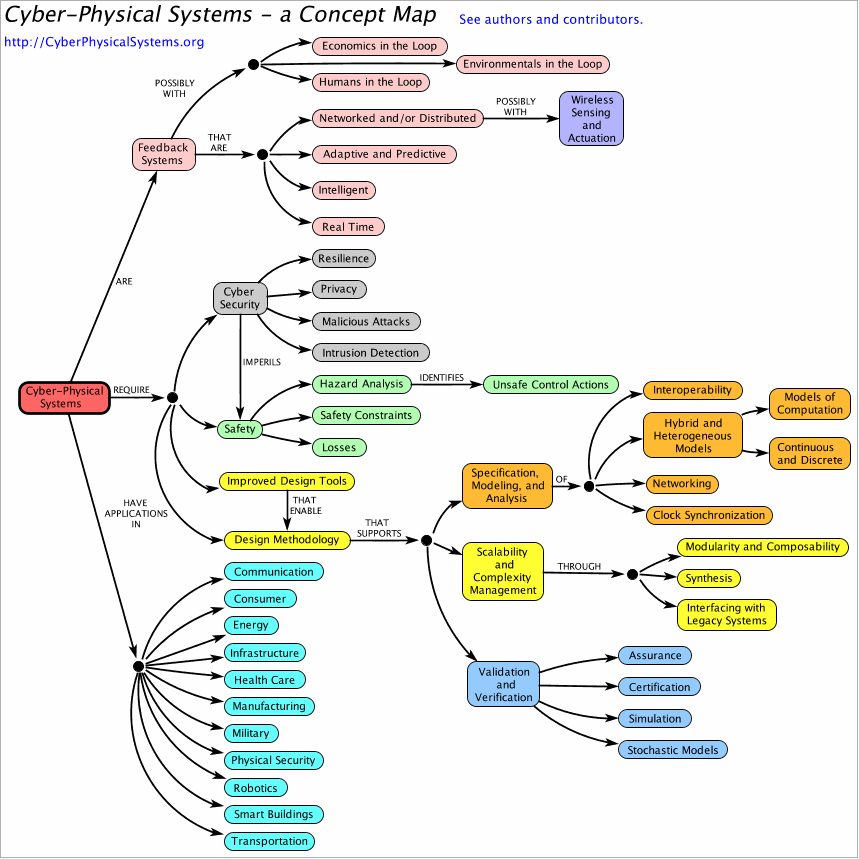
Why do we need Industry 4.0?
Simply said, Industry 4.0 is the much-needed digital transformation that manufacturing firms and value accumulating processes in many industries should undergo to sustain and shine in today’s industrial realm. This means not only digitising the business models, but it also means catching up with markets that are now prone to change overnight. Market changes are so instantaneous now, the reason behind it is also-unsurprisingly- technology.
Why are products a key driver in today’s industrial world?
Technology provided so many choices, endless to be precise so that every chance a person gets to introduce innovative products, the market would use the best product as a yardstick to measure others, hence, completely transforming the minds of the market thread in an instant. Industry 4.0 technologies give the ability for industry 4.0 companies to catch up with this ‘pace of innovation’ and be resilient to disruptive instigations while giving you the power to control the key driver to innovation: ‘innovative products’.
Products are the key where businesses meet the market, so, it is the primary element of the transaction that decides how competitive and how preferred you are in the market. Innovative products are smaller in size, advanced in anatomies, and much smarter. Products must be delivered in no time, even individualised products. Therefore, production life cycles must be reliant on new embedded technologies that interconnect all subsystems into one holistic matrix.
Some of the other advantages that are granted in Industry 4.0 are:
- It makes the managerial teams work collaboratively and with transparency
- Detecting, prioritising and predicting issues are never made easier
- Unlock full growth in businesses in respective industries
- Innovation unlocked with new research data to develop the new invention and personalised products for customers
- Optimisation in the functionalities of supply chains and logistics
- Guaranteed business continuity because of advanced monitoring, maintenance, and predictive systems
- Employee retention due to better working conditions
- Automation of every system while increasing productivity and more.
Industry 4.0 Solutions that facilitate discrete industries
Given below are some of the most apprehended technologies used in Industry 4.0 by smart companies to advance plant-wide functionality and mitigate many related managerial and operational efforts. May it be an individual machine, a product line, or an enterprise Industry 4.0 solutions optimise everything to be better, smarter, and more integrated within the industrial infrastructure that they are supposed to utilise.
Big Data Analytics industry 4.0
Big Data, as the term denotes, means mausoleum Data collections that are generated by sensors and actuators when equipment is functioning. For example, bulks of Big Data are generated when a robot moves its arm up and down. In Industry 4.0, technologies are housed to analyse these perpetual data streams to gather intel, by unboxing data fluctuations that weren’t revealed before and grasp the business intelligence that is vital in surviving in the market demands. These technologies are called ‘Big Data Analytics Systems’. Some resolutions that can be made by companies while using Big Data Analytics are:
- Reducing the expenditures that are allocated for needless purposes
- To make decisions faster and more agile by thoroughly studying the business’s field of interest and the crowd
- To research about building new innovative products and provide better assistive services
Predictive Maintenance 4.0
This technology is glorified especially in the fields of asset managing and maintenance and is now used by a plethora of industries to keep their systems running continuously. This technology is used by managers to predict machine failures and prioritise machines from critical to fully-functioning so that the company would not cease to reap benefits regardless of the downtimes. Predictive maintenance systems can be integrated into management systems to check for machine behaviours and different parameters can be fed to identify the propensity of the machine to work under changing environments. We can also identify Predictive Maintenance as the most reliable and statistical solution provider in foreseeing unprecedented failures through real-time condition monitoring and regression analytics. The advantages of using Predictive Maintenance are:
- Smarter detection of data patterns
- Optimise machine processes and performances through valid logical reasoning
- Achieve improved interrelation and collective control of equipment
- Monitor real-time progress to detect Key Performance Indicators and more
Industrial Internet of Things in Industry 4.0
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the technology that merges all assets, processes, stakeholders, services, data, and everything in an enterprise to one big digital mesh via cloud-based machines. The sole purpose of this integration is to increase the efficiency of the business endeavours and provide a healthy synergy between elements to facilitate industries. The quintessential Cyber-Physical Systems are enabled by IIoT for bringing physical systems online by unleashing interoperability between ‘things’ in the company to outcompete manual labour systems by automated mass manufacturing systems that can function around the clock and be controlled, secured, analysed remotely by plant maintainers or asset managers.
Integrative Industry 4.0 Technologies
Vertical and horizontal integration can be unlocked to connect the fragmented IT infrastructures of a business in Industry 4.0. It is an over-arching technology that is enabled by sensors, control systems, communication technologies, and other applications to allow a smooth flow of data in and out of the company. It enables growing value chains and universally integrated networks that are useful in understanding the level of competence required by a product and customer preferences. This technology can therefore be regarded as the backbone of a Smart Company. The specialties in integration in Industry 4.0 from other Industrial Revolutions are:
- Allowing strong orchestration between the end-to-end supply chains and help in providing actionable insights through analysing a variety of data types.
- With vertical integration, the production network would encompass well- defined properties such as performance desired statuses, minimal downtime schemas, and cost allocations per lots.
- Horizontal integration allows the whole company to integrate with the functions that are done in one department, ultimately collectively fostering all systems into one holistic system.
Artificial Intelligence
Within the Industry 4.0 paradigm, artificial intelligence is commonly termed to define an intelligent simulation of human intelligence in machines so they could think or act like humans. This technology plays main roles in predicting, robot-human collaboration, designing, and adaptation, and is celebrated as the driving force of the new age of industrial excellence. Manufacturers of all stripes can use this technology as
- a predictive yield to understand marketing standards and behaviours,
- predicting the operations and functionalities of the in-house machinery,
- permeate from internal business adaptation to entire ecosystems adaptations,
- and to design cutting-edge products too.
Industry 4.0 Cybersecurity
Given below is an illustration of the statistics circulated by the Internet Crime Complaint Centre (IC3) for the year 2019 that was posted by statista.com. The data consists of cybercrime reports that were recorded in America under different Cyber Threat categories in 2019. Click here to view more statistical findings of cyberthreats.
Every year the rate of cyberthreats amplifies in America, and it keeps sprouting around the world. These threats if not controlled keenly, many industries face a lot of financial threats, brand damages, trust-breaking, and more harms that can even threaten the sustenance of enterprises at large. Industry 4.0 anti-cyber-attack measures are therefore an indispensable technological security system for all industries alike. Such technologies can:
- Seamlessly integrate with legacy systems, regulation directives, and company standards
- Can mitigate threats and learn to adapt by facing them
- Activates in real-time when malware or possible breach is detected
- Protect all primary and third-party components (check whether all machines are updated)
- Is applicable for any device with any computational or energy limitation and even any sort of market devices
Edge Computing 4.0
Edge computing can be identified as a distributed computing system that amalgamates information processes on the verge of the network system that would either produce or consume the information. It generates and processes the data after the data is at the edge of the client’s end, rather than processing the data always at a central data processing centre. This makes Edge Computing one of the fastest data streaming mechanisms. Edge devices inherit the functional responsibility to interconnect the system to the cloud through data transmitting protocol. The purposes behind this cheek-to-cheek processing are:
- decreasing the latency of the data streams,
- increasing the potential of cybersecurity measures,
- increase the analytical powers of companies,
- expanding the interoperability of the cyber-physical systems and
- reducing data storage costs
Industry 4.0 Cloud Computing
One of the primary technologies that enabled Industry 4.0 is Cloud Computing. Big data analytics, IIoT, and other IT-enabled services are made plausible through this technology. It is regarded as the gateway for smart manufacturing where smart machines are interconnected to the cloud to allow transparency in processes. Most industry 4.0 cloud computing systems have the multitenancy to deliver computing services to many users simultaneously. Public clouds are openly accessible by users rather than installing an expensive system to save usually tackled data. Private and hybrid clouds are also used by enterprises that use chunks of Big Data every day. Some of the most common examples of cloud-driven services are:
- YouTube
- Netflix
- Google Drive etc
Additive Manufacturing and Simulation
Digital Simulation provides the basis for additive manufacturing, to use virtual models to construct replicas of assets either in the digital world or out of silicon to mitigate the time, efforts, and expenditures that companies invest in test runs and maintenance programs. Many industries massively use this Industry 4.0 technology to predict probable downtimes, foresee danger, detect KPIs in machines, quickly identify abnormal data fluctuations, and many more. Technologies such as Digital Twin, 3D printing, Embedded Predictive Systems, Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality and Condition Checking Systems work hand in hand to provide an eventful simulation experience for their users to construct, manage and monitor their assets as needed.
Advanced Robots
Industry 4.0 Robots are advanced in handling complicated and delicate tasks on their own. They can be programmed with new technologies and highly responsive sensors to detect miscellaneous data flows in real-time allowing them to learn, work faster and work ‘with humans’ instead ‘for humans’. Collaborative Robots (“Cobots”), autonomous mobile robots are now gaining likeness in many industries for their amazing capacities in collaborating, spot-on precisions, and progressive machine learning abilities.
These robots can:
- complete tasks intelligently with minimal human intervention
- avoid obstacles if met during work at a safe distance
- be interconnected via IIoT to enable remote access and control over their actions etc.
Industries that are enlightened by Industry 4.0 technologies
Given below is a very summated table on 10 industries that are facilitated by Industry 4.0. Please note that they are not the only industries and the reasons stated-5 per industry- are the main but not the only reasons why these industries adopt Industry 4.0 technologies.
[table id=11 /]
Challenges faced in Industry 4.0
With the plethora of advantages and transitions and benefits that Industry 4.0 contributes to us, there are challenges here and there that would be challenging for some businesses. As the impact of Industry 4.0 is an obvious inevitable guest to our lives, we should acknowledge the barriers that we have to break to get the optimal support of these technologies too.
- One of the main challenges that people face sprouted from misinterpretation. Many misinterpret that adopting industrial 4.0 technologies itself is enough for the growth of an enterprise. Or at least the advanced levels in physical technologies. But having veterans to handle these systems is as important as investing in the technologies. Optimising the labour in your companies is now vital, employees can be taught to handle systems, monitor and intervene when humans are required to.
- Implementing technological systems is also vital and is very expensive if you don’t know how to do it. Contact Industry 4.0 consultancy service providers to learn the best ways to choose and implement the right choice of technology to your systems. Especially if a business is an SME managing resource when adopting technologies is very crucial.
- Smart factories take time to adopt sensor technologies, it is a complex system that requires effort and time to understand before getting the full service out of it. Make sure your staff goes through enough training to apprehend the advantages and methods of operating with sensor systems before they use it in the field.
- Interconnectivity can also lead to many security uncertainties since the more the managerial systems are interconnected the threats or cyberattacks are amplified. Therefore, every company must look out for reliable and authentic cybersecurity systems.
- Adapting to new competencies, systems, cultures, and finding new resolutions aligned with intelligence, innovation, and technology is very complex.
Industry 4.0 has given industries the luxury to be available, at any time in any place regardless of all physical and knowledge boundaries. It is not surprising that technologies keep changing and developing with time and the latest technologies themselves provide us with boundless efficacies. We are surfing our lives, businesses and every aspect around us towards a whirl concentrated with opportunities and shortcuts because of technology.
This technological wave is binding us with machines in such a way that we are now incompetent without them. Even though many people are still in denial to accept the luxuries of Industry 4.0, companies and countries that already house recent digital solutions are already thriving in the world. Therefore, embrace the Industry 4.0 technologies by acknowledging, learning, and using them to simply be updated and spend an effortless day at home or work.
