Commemorated around the world as one of the leading financial hubs that have a thriving digital economy with successful commodity trading practices and more, Singapore has left a true mark of success within the past few decades. It is evident that the industrial realm in Singapore is playing a precise role and generates productive results proactively to support this cause, but how? How did Singapore soar up to the highest rankings in terms of economy, higher standards of industrial performance while being a country with better living standards at every level? This is because Singapore’s journey to success cannot be distinguished from technology- they have a strong synergy. Harnessing modern technology to transform the Nation into a Smart Nation digitally, leads to being equipped with concepts like Smart Homes, Smart Governments, and Smart Factories.
Industrially speaking, technologies that fall unto IIoT (Industrial IoT) and Automation have paved the way to establish Smart Factories in Industry 4.0 – where the physical and digital worlds come together. Even though the living standards were also highly facilitated by technological developments, we will be focusing on how Singapore dreamed for industrial development and how they geared up to promote their dreams to be real-life success stories. Singapore Manufacturing Enterprises advanced by collating agility, proactivity, interconnectivity, along with cutting-edge factory optimisation. Industries are now at the brink of changing and achieving more pristine goals faster and with better success rates in the digital age. Therefore, we prepared this guide for readers who need to unravel the true potential that technology has to serve a nation to be in the Industry 4.0-standard and how Singapore transformed their Nation accordingly.
Before we continue, let us view how technology was accessed and implemented in Singapore in the 1900s.
Technological history of Singapore
In the 1960s the commercial sector of Singapore contributed to 11% of its economy. It was during this century robust electronic manufacturing made its advent to Singapore. However, with urbanisation, technology disrupted many changes in the 1980s which churned the manufacturing industry and rebuilt it to be faster and better. The Government of Singapore never tended to overlook the advantages that technology and innovation can serve to build their country to be whole and to strive for success. It is fascinating to see how technology has always been a counterpart for Singapore, for they implemented events to collate technology into their lifestyles even in the 1980s through Digital Initiative- namely, the National Computerisation Programme. Influenced by this Initiative the NCB (National Computer Board) made its advent to the as a new public body to the Singapore Government in September 1981, which is also the predecessor of the current GovTech team of Singapore. It was during this time; Singapore took the pride to:
- Computerised Civil Services of Singapore (this approach was a turning point where technology supercharged the government services- it initially facilitated ten government ministries to be precise)
- Coordinate with Computer Education and Training
- and develop the local Computer Services Industry
- 1981 – Computerisation of The Civil Services
- 1987 – Singapore’s advent to the Global Networking Community
- 1988 – The use of mobile phones in Singapore
- 1989 – TradeNet mitigates trade document processing
- 1998 – IT professions rose rapidly allowing new job opportunities in Singapore
- 1999 – NCB merged with Telecommunications Authority of Singapore (TAS) and renamed the body as Infocommunications Development Authority of Singapore (IDA)
DID YOU KNOW: In 1988, the Apple Computer established a manufacturing facility for Mac Computers in Singapore by investing S$ 25 million.
What is Advanced Manufacturing?
Singapore stays ahead of the curve of countries that adopt technology to maximise the capabilities of their industrial realms. This is precisely where Advanced Manufacturing comes in; it serves the idea of technological upgrades undergone by manufacturing technologies when Automation and digitalisation empower them to redefine manufacturing models to reap massive ROIs with better factory performances. The technologies used by Advanced Manufacturing can be broken down into two main categories as:
- Industrial IoT: IIoT refers to the digitisation of machines and all elements in the manufacturing ecosystems through transparency and interconnectivity. IIOT is an amalgamation of Cloud Computing, Smart Components, Simulation, Cyber Security, Machine Learning, AR and more.
- Automation: Automation refers to the technologies that allow machines to grasp data, learn and adapt to controlled environments. This sector refers to components such as PLC, Human-machine interfacing, Supervisory controls, Data acquisition, AGV technology, Robot technology, Sensor technologies, Instrumentation and more.
In short, the rate of successfully adopting Advanced Manufacturing practices reflects how ready any industrial site would be Industry 4.0. It redefines how products are manufactured and how value and supply chains are changed for betterment.
The infographic below shows you a well-versed diagram of what Advanced Manufacturing fosters. Some examples of the technology partners and manufacturing counterparts that are collaborating to impose better Manufacturing conditions in Singapore are mentioned too. This graphic was posted by edb.gov.sg.
The EDB is an agency of Singapore’s Ministry of Trade and Industry that enhances the industrial efficacies and speeds up harnessing innovation and talent to facilitate the businesses of Singapore; for better economic growth and sustainability.
Strategies Used by Singapore to implement Smart Factory Transitions

Smart Industry Readiness Index
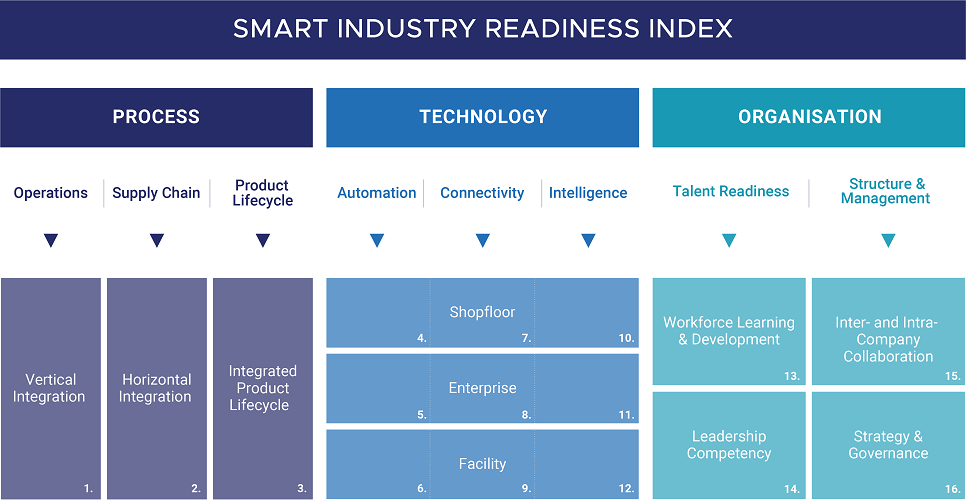
Given below are two tools that gear up a company to scale their performances according to the Smart Industry Readiness Index.
The Assessment Matrix
The Assessment Matrix is a self-diagnostic tool to determine the start, scale and success of the companies between the 16 dimensions. It shows 6 progressive bands to elaborate on how companies can systematically mature in adopting technology by qualifying for each dimension one by one. Companies can equip the Assessment Matrix to assess their current standing in successful digital transformation. This tool pinpoints the gaps companies have between their journey and booming technology adoption industry 4.0
The Prioritisation Matrix
Companies can use this management planning tool to architect the technology advancing roadmap to expedite the impaction of the organisation by the dimensions in the index. It follows the following formula to measure the improvement of a brand.
Industry Transformation Maps
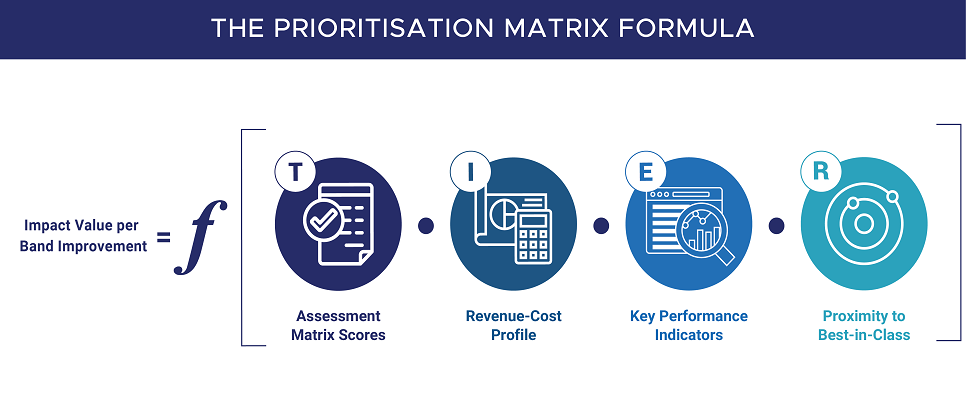
Launched in 2016 by Singapore, Industry Transformation Maps (ITMs) were enabled via a project worth of S$ 4.5 billion to roadmap the advancement of 20+ industries in Singapore which are clustered into 6 main groups. It addresses sector-specific disputes related to industries, firms, trade associations and the government when the Singapore Industries are surfing towards Digital Transformation to achieve the Industry 4.0 standards comprehensively. ITMs can, therefore, be defined as integrative maps to drive industries towards optimal digital transformation using Automation and other modern technologies.
The industries considered in this incentive are responsible for accounting for an economic output of 80% of the Gross Domestic Product Per Capita in Singapore. These industries are broken down into clusters to mitigate better control and responsibility bearing by the government agencies. The tripartite partners (unions, businesses and the government) access how the industries will grow and extract data related to their productivity, jobs and skills, trading practices, innovation and internationalisation. The 6 clusters of the 23 industries and their lead agencies are displayed in the table given below,
Smart Nation Initiative
Modern technologies develop the civil services of Singapore, they also took the leading hand in mitigating the lifestyles of the citizens through the ‘Smart Nation’ concept. ‘Smart Nation’ defines the beneficial transformation that Singapore undergoes at the expense of a slight disruption in the daily lifestyles of the citizens. For this purpose, the Smart Nation and Digital Government Office have even shared a series of programmes to help children, youth, young parents, working adults and seniors apprehend and familiarise with the latest technologies that are making their way to supercharge Singapore.
However, more strategies were implemented by the Smart Nation and Digital Government Office of Singapore; some of the strategies that were exerted under the Smart Nation concept in Singapore are explained below.
1. National Artificial Intelligence Strategy
Singapore invested in the National Artificial Intelligence (AI) Strategy mainly allows researchers, collaborators or businesspeople to be well-versed in 4 AI-related areas.
- Being well-versed about the 5 national AI projects that pick the limitations of 5 main industries, namely,
- Healthcare Industry,
- Education Industry,
- Transport and Logistics Industry,
- Smart Cities and Estates Industry, and
- National Safety and Security
- To redefine the managerial and operational endeavours of these 5 areas with modern technology.
- On how Singapore Businesses can transform their businesses with AI
- To invite contributors to participate in Singapore’s AI ecosystem.
- And finally, learn about the propensity of the AI technologies adopted by Singapore.
Please click here to learn more about National Artificial Intelligence Strategy in Singapore, or here to download a summated brochure.
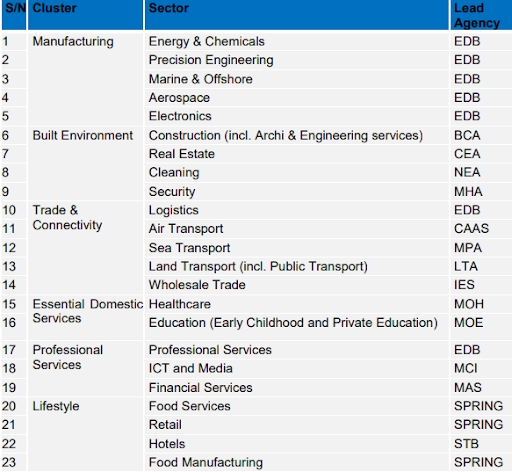
2. The Digital Government Blueprint launched by GovTech in Singapore
The Government of Singapore has taken systematic initiatives to digitally transform the public services exerted by the government through technology- with the target of building Industry 4.0 empowered smart nation in Singapore. The Digital Government Blueprint of Singapore, abbreviated as DGB, is an official approach circulated by the government to elaborate on how Singapore will harness technologies to broaden the technologically opportunistic environment to strengthen Singapore’s digital economies and societies. This statement was summated to a tag line as “Digital to the Core and Served with Heart” by the government to show a passionate drive towards Industry 4.0. This principle elaborates on how the Singapore government will use data, interconnection and re-architect existing technological structures with modern technologies. Also, elevate their sophisticated applications to be user-friendly and advantageous for their citizens. Click here to read a summarised brochure to learn more on DGB. The image below was illustrated in Techgov.sg to display a brief understanding of DGB.
3. Digital Service Standards to reach DGB by agencies
The Singapore Government has also implemented a set of quality-standards to guide agencies who wish to elevate their in-house digital service to meet with the ideas expressed by the DGB. This was a move made to help the agencies to adopt new technologies comprehensively without blindly targeting towards Industry adaptation. It narrates the main components that agencies must refer to; they are:
- What are DSS and DGB and who must follow them
- How to review, plan and gain ownership of the digital services
- And three principles to initiate frontend user interface design;
- Principle 1: Intuitive design and Usability
- Principle 2: Accessibility and Inclusivity
- Principle 3: Relevance and Consistency
Click here to read the public released version of the Digital Service Standards of Singapore.
AdResults of such strategies – are there any drawbacks?d Your Heading Text Here
Adapting the Singapore Nations to qualify the Industry 4.0 qualifications is a buzzing topic in the industrial and technological worlds. Singapore estimates that with these incentives and redefinition of the industrial endeavours they can boost the productivity rates of labourers 30% more than 2017 stats by 2024. Singapore was one of the top countries to identify that being alienated from technology handicaps a country’s economic growth and that the best and latest way to surpass this constraint is through adopting technology to be Industry 4.0 recognised. Along with the incentives practised circulated in Singapore, initiatives are taken by both private and government sector businesses to acknowledge the gaps between proper technological understanding by companies and explore ways in abridging this unknowingness or defected adaptation of technological solutions.
For example, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research) presented two model factories, namely SIMTech Model Factory and ARTC Model Factory, to present a ‘live’ production environment so that companies can understand how technology basically transforms a factory to gain more with less effort, time and money. It ensures plant-wide visibility and real-time feedback generations to help plant managers and decision-makers to gain end-to-end control in their factories. They were able to grasp timely responses to pool in new insights gained by real-time data streams of factory equipment. These model factories embodied: Centralised Control Rooms, Virtual Manufacturing labs, Digitised factory Floors and more. It further elaborates on the benefits of a Smart Factory that could be gained if factories were optimally fostering modern technologies like empowering factory operators to make comprehensive and proactive decisions, optimising the monitoring capabilities of the production lines, enhancing the safety of the factory floor and optimally handling and delivering of inventories. It basically improved end-to-end manufacturing ecosystems and trialled comprehensive visibility on how advantageous a Smart Factory can be.
Also, adding to the challenge of being unaware, companies are also attested to misunderstand digitising the industrial sites as an IT project, it is more of a change that must be initiated, maintained and attained effectively. It is broader than just technologies being applied to make things more comfortable; it is a disruptive process that affects jobs at different levels. Therefore, it is vital that all the employees -higher or lower in the employment hierarchy- are being well-versed about what an effective digital change is and how it must be exerted. The BCG’s (Boston Consulting Group) Mr Lim has suggested three steps for effective change in technologically disruptive environments:
- Embracing all wins (small or big)
- Importance in recognising big or significant wins for the companies to change
- Making sure that the requisite Capabilities are in place
The Industry4.0 incentives did bring up challenges, as mentioned above. However, the collaborative measures and side-by-side awareness of the Singapore government and private sector businesses stepped forward to clarify these doubts, mitigating the exercise of the government strategies taken to transform the Nation to an Industry 4.0 Smart Nation.
Statistics of Manufacturing Companies before and after the advent of Industry 4.0
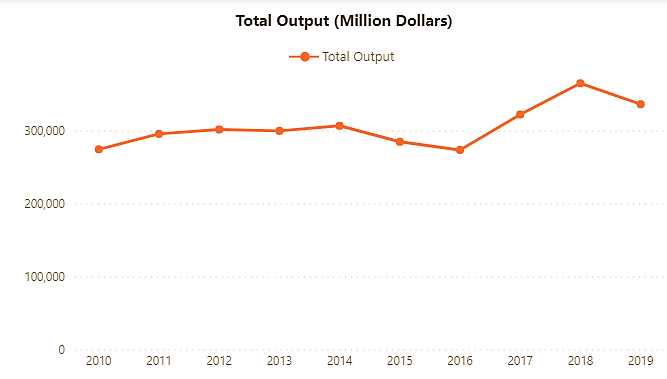
For additional Manufacturing sector information, click here to download a table that illustrates Business Expectations of the Manufacturing Sector – Business Sentiments for October 2020 – March 2021.
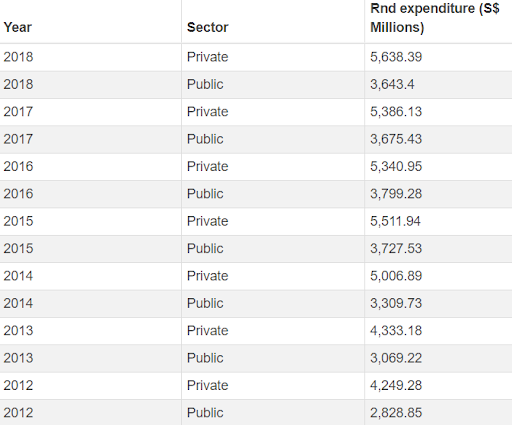
Also, given below is a table posted by the data.gov.sg on the expenditures incurred by the public and Private sector businesses from 2012 to 2018 in Singapore. It shows the rising rates on investments after the advent of the incentives, where companies of Singapore especially the private sector businesses invested a comparatively high amount of investment to research and developed their efforts for better productivity.
Singapore Industries that were influenced by Industry 4.0
- Aerospace Industry: With technological advancements, Singapore Aerospace sector became one of the largest and most diversified ecosystems in Asia. Advanced manufacturing engineering capabilities along with IIoT and automation technologies, this Industry tends to develop industrial level tech and provide support for exploring innovation faster. Singapore prepared for future workforces in the Aerospace Industry by upskilling and reskilling PMETs. 86 job roles would have career growth opportunities, and existing Professional Conversion Programmes (PCPs) will benefit more than 60 mid-career PMETs.
- Precision Engineering in Manufacturing Industry: Precision Engineering is a key-drive towards building Industry 4.0 Smart Factories. This sector fostered digital manufacturing platforms that elevated manufacturing capacities and supply chains in the plants. SMEs were assisted via technology when retooling and value-adding manufacturing efforts. Adopting modern technology in the manufacturing sector enabled Singapore to find new ways to grow with Robotics, Advanced Materials, Sensors, Additive Manufacturing and Lasers and Optics. By 2020, it was providing 3000 PMET digital manufacturing jobs.
- Marine and Offshore Industry: Technology uplifted Singapore’s Marine and Offshore Industry and provided them with the opportunity to meet future demands at the right time. They adopted the robotics and automation technologies to reduce labour force dependency and supercharge the productivity rates through smart marine and offshore engineering solutions. This sector is also reskilling 300+ PMETs through Professional Conversion Programmes (PCPs) since 2016.
- Electronic Industry: As Singapore is renowned for providing innovative digital solutions and technological roadmaps, the electronics industry was also advanced in the process of adopting Industry 4.0-driven solutions. It attracted high manufacturing activities and embraced robotics and Automation to add value for electronic manufacturing. This ultimately made Singapore an innovation hub for electronic products and solutions. Urban mobility, healthcare and other growth markets were diversified and mitigated with electronic advancements enabled by modern technologies too. It also allowed the new introduction of 2100 PMETs jobs by 2020 and shifting PMETs in Singapore to higher-value jobs through Electronic Industry Professional Conversion Programmes.
- Energy and Chemical Industry: Advanced manufacturing and other technological solutions mitigate the manufacturing, operational and precise managerial endeavours exerted by the Energy and Chemical Industry. It harnessed technologies to decrease the innovation cycle times and explore ways to evolve the products slate of speciality chemicals and value-added petrochemicals. By 2025, 1400 newly refined jobs will be introduced in the Energy and Chemical Industry.
Success stories of Giant Manufacturers guided by Industry 4.0 in Singapore
Procter and Gamble (P & G)
P & G is a giant consumer products manufacturing company that makes many order winning products such as Pantene, Olay, Safeguard and SK-II. This global enterprise researched in Singapore in 2017 by establishing a digital innovation centre. This movement technologically enhanced 3 core areas: e-analytics, supply chain processes and translation of digital strategies into scalable e-business models. The projects which are executed to research on better innovation facilities include:
- A S$ 250-million-project with 500 employees to innovatively research on P&G’s product categories. 250 hi-tech research laboratories are established through this project.
- A S$ 140-million-project that harnesses digital innovation to empower the working conditions of their manufacturing centre. It ensures transformation of the supply chains to be more generous in accuracy and efficiency, and it adopts predictive analytics, digital strategies and big data analytics to support their goals and overseas businesses across Asia.
Siemens
Siemens is one of the largest industrial manufacturing enterprises in Europe. This enterprise giant operates a digitalisation hub with exceptional integrative abilities in Singapore. This hub houses multidisciplinary experts to collaboratively assist the digital needs of their clientele in Asia and beyond. This effortlessly developed a roadmap for Siemens facilities to be digitalised. Once the operations were digitised, clients are provided with dashboards that display smart information from across the value chain mitigating the internal processes of the manufacturing plants. Siemens also contracted with Singapore making Singapore the first country in the world to pilot MindSphere. MindSphere is a cloud-best IoT OS that virtually interconnects machines and other physical infrastructure with the heed from data collected by millions of smart devices to generate innovative insights.
Smart Factory transitions Future proof or not?
Smart factory transitions are future-proof! There is no doubt about their authenticity and reliability because though it is a multi-year trip to 100% adoption of i4.0 smart factories. Singapore is patient and persistently reviews their industry-specific technological advances. Unions, Trade Associations and Chambers, or TAC, and other stakeholders in the industrial sector of Singapore are appointed periodically to check for anomalies, KPIs and further noteworthy analysis amidst the work-in-progress transformations. These approaches and the passionate drive of Singapore as a Nation will make sure that Industry 4.0 adoption is not-to-be-missed.
How will a future Smart Factory look in the future?
So, amidst all this excitement, a very tempting question that is asked by all curious readers will be, so what will smart factories look a few digital years ahead. But in reality, smart factories are already fully or partially in practice. One of the most distinctive features of a Smart Factory is Digital Twinning. Digital Twin technology has the propensity to create digital models of all the physical components in a factory- machine, device, robots, conveyor belts, even the factory’s infrastructure. These models will be interconnected digitally and shared into a cloud. This allows centralised control, real-time visualisation of the actual performances of the factory and optimise factory performance through its best possible conditions.
Advanced manufacturing also encourages Automation as much as advanced simulation. For example, when a job is assigned to the factories assembly sector, the Automated Guided Vehicles will be given instructions remotely. These machines can collect the required components from the storage, batch them up and transport them to each workstation without any human intervention at all. At the assembling station, robots will interact with their human counterparts and with other machines through M2M communication, while they are remotely supervised through advanced visual technologies to keep a real-time assessment on their work qualities and performance rates. Imagine a very urgent and crucial order is communicated to the assembling department. A future-proof smart factory would have the tendency to reschedule the whole manufacturing process automatically by the cloud-based MES systems. Process schedules will meet the deadlines without suffering any downtime or insufficiency whatsoever.
Expanding the factory attributes regionally or globally is also made even easier through interconnection, with the global market trends and demands, adopting an Industry 4.0-assured Smart Factory will soon be inevitable. Other technologies like Additive Manufacturing, Cybersecurity Protocols, Predictive Analytics, Augmented Reality, and more will also be housed in Smart Factories to be fully-geared in the digital age.
Singapore today
- Singapore, since their journey with Industry 4.0 derivatives since 2017, is now recognised as the best tech hub in Southeast Asia and the second in Asia.
- They are also the first to enable digital transformation in Asia, even before Japan, Hong Kong, South Korea and China.
- Singapore is the global first in Smart City Performance. It has the best digital infrastructure in Asia, where over 50% of the data centre capacities of SEA belongs to Singapore.
- Singapore’s Changi Airport is considered as the most connected airport for it is connected to 100+ airlines, serving more than 100 countries by flying to 400+ cities around the world. Per day Changi Airport connects over 1000 flights where over 60 million passengers are served every year.
- Also, it enables cutting-edge outdoor coverage to more than 100 million devices in their Nation.
- All these technological advancements successfully led in Singapore being the first in ease of doing business in Asia and 2nd in the world.
- With interconnection Singapore allows anyone to start a business in Singapore within just one and a half days!
- Today Singapore is the innovative economy in SEA and the third in the world.
- It is the 1st for IP protection in the Asian continent and the 3rd in the world.24+ Free Trade agreements
- In 2018, Singapore ranked 2nd in the Readiness for the Future of Production Report in the World Economic Forum.
- Singapore is now the 4th largest hi-tech product Exporter.
- Singapore has an evolved workforce where PMETs are toned to future-proof working practices with well-trained skill sets. Singapore shared a SkillsFuture programme to tone the industry-relevant skills of employees who are influenced by Advanced Manufacturing. Also, a strong tripartite (Unions, Singapore government and companies) upskills and reskills the workforce in Singapore every day.
Conclusion
Singapore is a country that suffered from piling on operational costs, a detrimental domestic labour crunch, and the Singapore Currency was weakening, all this happened not so long ago. But Singapore pushed through all limitations and took the bold Initiative to welcome transitions to make their nations, homes and factories to be resilient to anchoring down inefficacies. Today technology adoption is widespread in Singapore. Even though Industry 4.0 transitions are regarded as a new trend, the best nation-wide development in vogue, Singapore is too familiar with it. Their industrial, societal and governmental ecosystems, networking systems, and even the most minute physical processes are being revamped, evolved and refined by technology. The critical drives are ‘Enthusiasm’, ‘Passion’ and ‘Determination’. Singapore is now recognised as a technology wielder around the world.
It is also important to note that regardless of the onslaught of IIoT and Automation, the Singapore workforce still remains as the heart of their industries. All the Industry 4.0-specific incentives that were exerted by Singapore requires technology along with experienced human hands. Suppose a country is striving for the best for its citizens but is disheartened or doubtful in disrupting their existing processes. In that case, Singapore can be introduced as the best example for national endeavours that inspire countries to wilfully and confidently adopt Industry 4.0 transformation to evolve to be global winners digitally.
