On the 18th of August 2020, SpaceX launched Falcon 9 rocket homing 58 satellites were launched into space. There are almost 655 satellites (each weighing 227kg) launched afore, and the next planned project is dated in September 2020 with 120 more satellites dispersed in 2 consecutive launches (two launches for each month). All these satellites will be located in 550km-low earth orbit. This mission is an ambitious new project, and it is called Starlink, which aims to provide high-quality broadband internet to the most isolated and rural parts of the planet, it would also be a reason in providing low latency connectivity to already well-connected cities.
The initial plan is to cover the USA and Canada, and the rest of the world will eventually be covered in the latter part of the year 2024. But given the current uncertain situation arisen due to COVID-19 the project might be dragged for two more years, along with NASA’s Artemis program (sending the first women to the Lunar surface) and Elon Musk’s colonising Mars program (Occupy Mars).
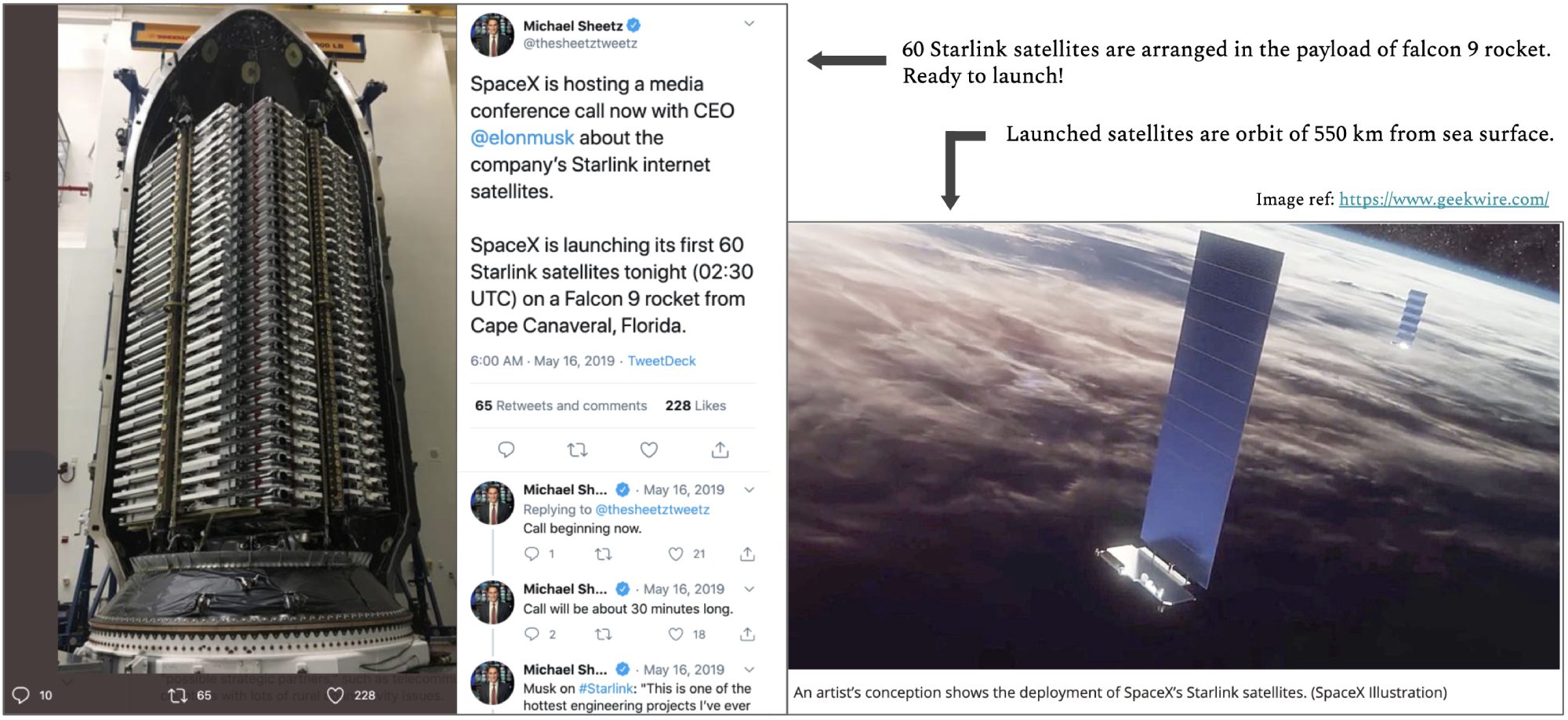
SpaceX has around 12,000 satellites and has planned to launch them over the next decade, and this will dramatically increase the total number of satellites around the earth’s orbit. This project is going to cost SpaceX billions of dollars, which must be fueled by a good productive reason for carrying out a risky and pricey project.
How is Starlink establishing internet connectivity?
Each satellite will be equipped with lasers. The lasers used are similar to fibre optic cables that are mainly used at houses and offices. It will use light pulses to transmit information between satellites. Transmitting with light in space offers one massive advantage over transmitting with light here on earth. The speed of light emitted by every material varies from one to another in different settings; in fact, light travels 33% slower in glass than in a vacuum, as mentioned below:
- ~ 300,000 km/sec in Vacuum
- ~ 225,000 km/sec in Water
- ~ 200,000 km/sec in Glass
This offers Starlink one not-to-be-missed advantage that can transmit data faster than any other network existed. It provides the potential of lower latency information transmission over a long distance.
The importance of the transmission latency in businesses
For example, when a user in London wants to view the newly adjusted price of a stock on the NASDAQ from the New York stock exchange. The information required uses a typical route to travel, let’s say through the AC-2 subsea cable, which has a return journey of about 12,800 kilometres to make through the glass fibre optic cable from London to New York and again back to London).
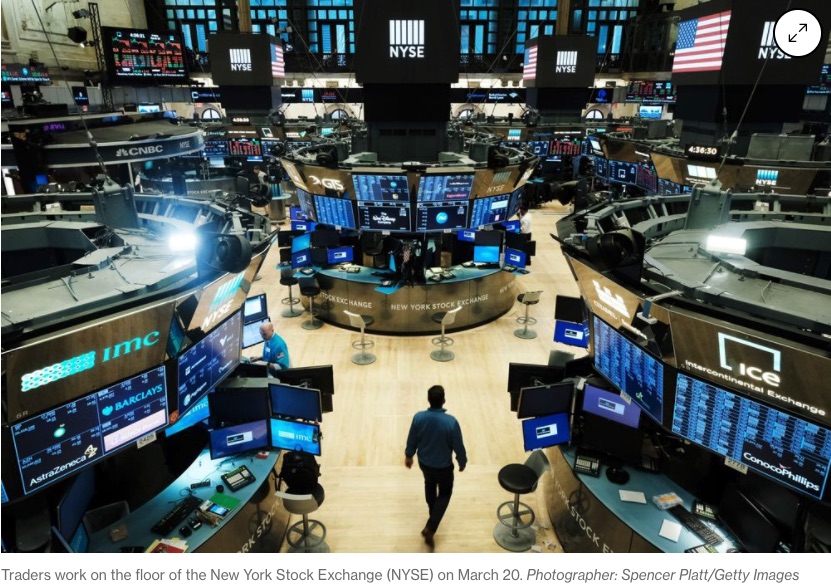

The data packet will take roughly 0.064 seconds to make the round trip, and thus has a latency of 0.064 seconds (64 milliseconds). With the additional processes such as:
- Latency conversion of light signals to electrical signals at both ends of the optical cable
- Traffic queues
- Transfer to our final computer terminal
This entire process comes around about 80 milliseconds.
However, the Starlink latency will be lesser during the up and down linking process, where we need to transfer our information to satellites from the earth. Once the data received by one of the Starlink satellite, the Starlink satellites in the earth orbit will horizontally communicate, where they transmit information between satellites using lasers. The process of this speed is equal to the speed of light in vacuum.
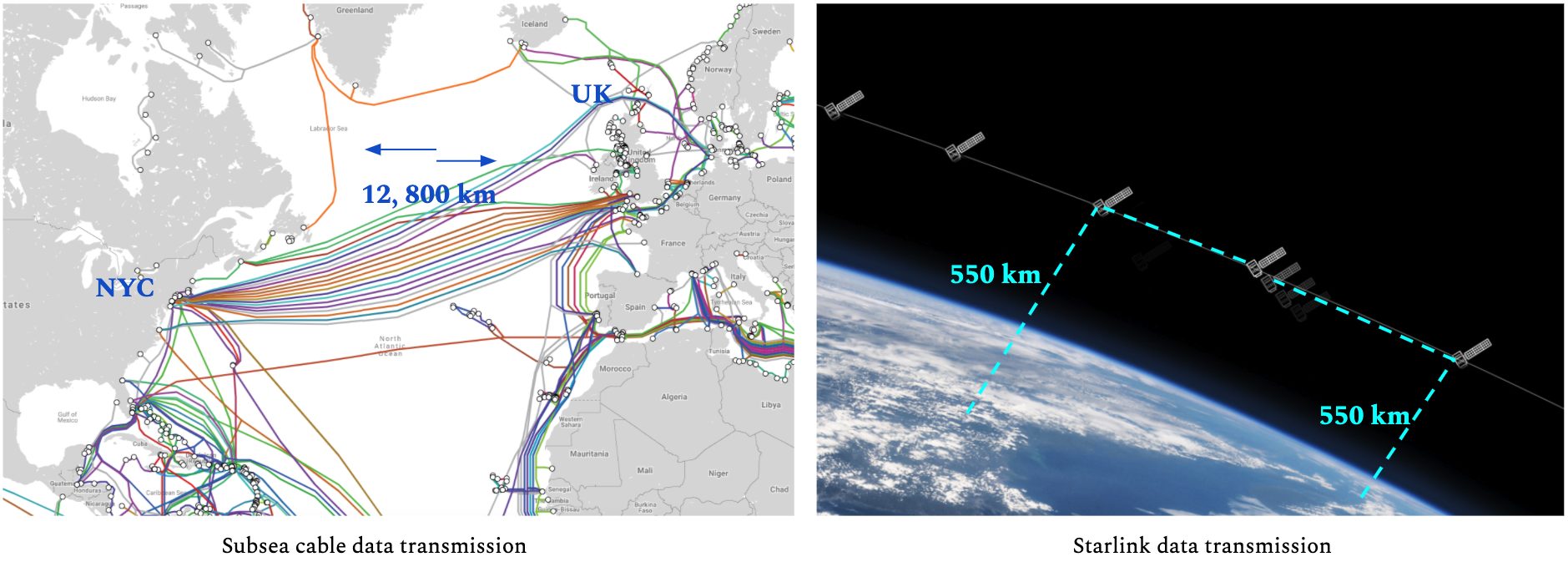
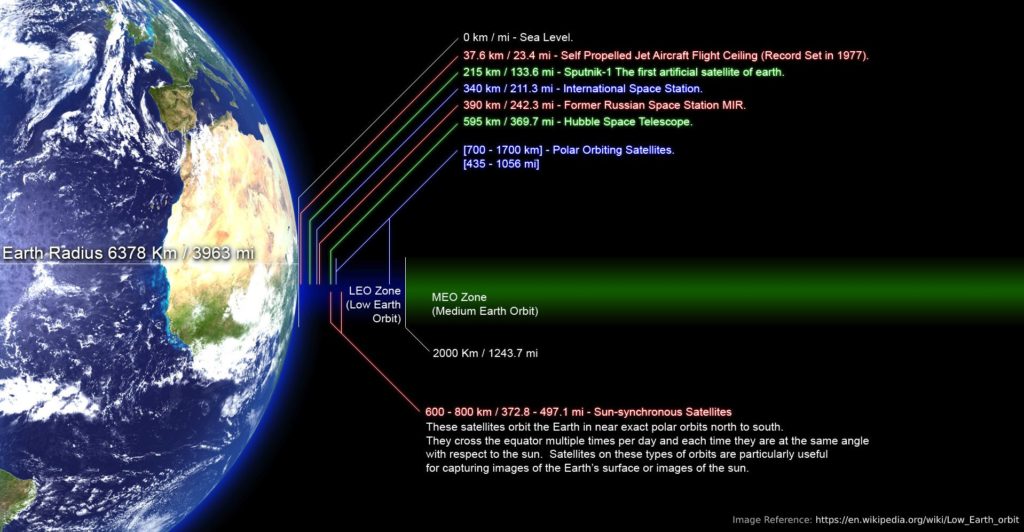
With a 550-kilometre orbit, each satellite can cover a circular area with a radius of 500 kilometres. (So, technically, Singapore needs 2 of the Starlink satellites to cover up Singapore completely). Initially, at SpaceX’s originally planned orbit this coverage had a radius of 1060 kilometres. Lowering the altitude of a satellite decreases the area it can cover, but also reduces the latency. So, the altitude of 550 Km is the ideal value by considering latency and covering up radius.
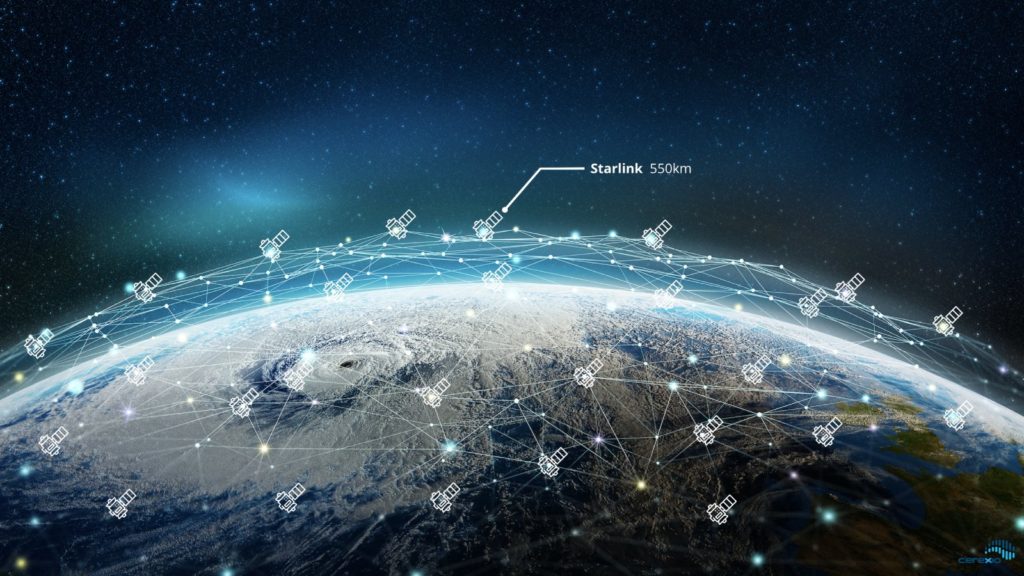
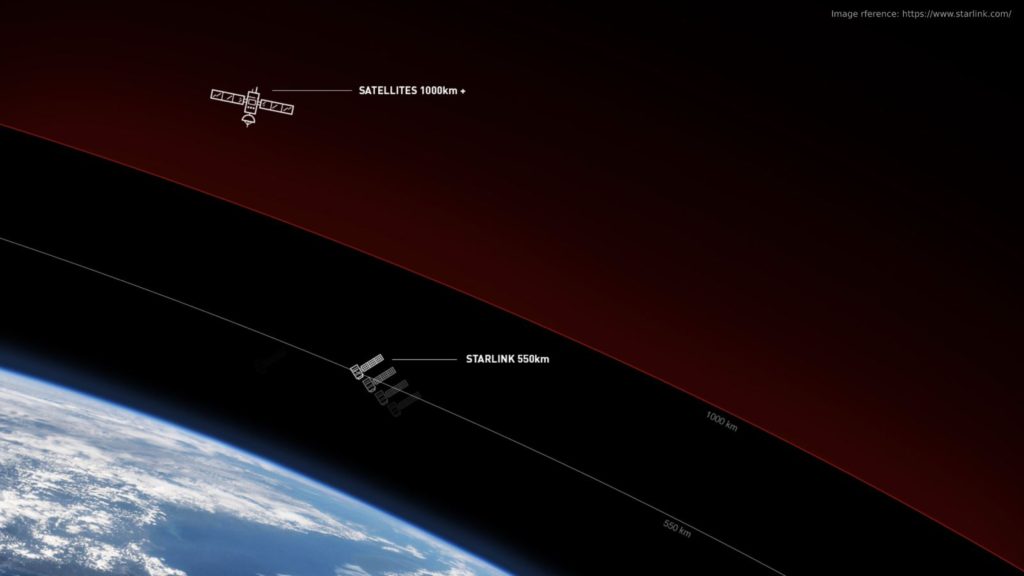


This is particularly noticeable for typical communications satellites operating in geostationary orbit at an altitude of about 35,000+ kilometres. The time it takes data to travel up to this satellite and back down, the speed of light is around 235 milliseconds. However, since Starlink intends to operate at a much lower altitude, the up and down link theoretical latency could be as low as 3.6 milliseconds only. This is why SpaceX needs a swarm of satellites in their constellation in order to provide worldwide coverage.
If Starlink is transmitting from London to New York and back, with the shortest path possible, using the speed of light in a vacuum as transfer speed, latency as low as 43 milliseconds can be met. Even when taking the shortest route possible with subsea optic fibre (which does not exist), this would take about 55 milliseconds, amounting a 28% decrease in speed. The actual current return trip time for your average is about 80 milliseconds, as explained above.
This is an easy 77% decrease in speed. This is a massive deal for the two financial markets working out of these cities, with millions of dollars being moved in fractions of a second, having a lower latency would provide a massive advantage in capitalising price swings.
Does this majorly affect the Financial Market? Can a few milliseconds affect the business?
It is a definite yes. It is undoubtedly a huge deal!
The Hibernian Express cable is a privately owned optic cable that is currently the lowest latency connection between the NY4 data centre in Secaucus, New Jersey and the LD4 data centre in Slough, England. Round trip is just 59.95 milliseconds. The previous shortest time of transmission was held by the AC-1 cable at 65 milliseconds. At a construction cost of 300 million dollars, these five milliseconds increase in speed was justified by the private cable to just connect across the Atlantic.
This showcases how much time-sensitive industries will be willing to pay to save 17 milliseconds increase with speed. That is why most of the real-time businesses, streaming technologies are investing innumerable amount for reducing the latency. Now the world is slowly stepping into 5G for high-speed internet on the surface level of the earth. But, Starlink is always far ahead to provide high-speed and ultra-low latency internet among continents as well as villages and remote areas.
With a 550-kilometres orbit, each satellite can cover a circular area with a radius of 500 kilometres. It will be even more worthy when its users realise it has time differential advancements with increased transmission distances. New York to London is a relatively short distance! The improvements would be even more pronounced for a London to Singapore transmission, for every additional kilometre we travel the potential gains in speed increase rapidly.
A tremendous advantage for all businesses
SpaceX offers ultra-low latency data communication beyond/within borders. So, you can transmit a large volume of data faster than ever before. Not only stock trading, but also many other industries such as Video Conferencing, Multiplayer Gaming, CDNs, Digital Twins, Condition Monitoring, MES 4.0 System, Maritime, Aviation, Supply Chains & Warehousing, and more other businesses will flourish with this splendid advantage offered by Starlink.
You need a robust message handler (a message broker)
Once the data is transmitted and delivered via the internet, there must be a mechanism to handle them. Cerexio-Axon is a multi-protocol message broker, and it has its built-in proprietary methods to handle more than a billion events in a single second. It enables you to build your data streaming network. Its exclusive algorithms enable you for high-speed data streaming bidirectionally.
Cerexio Axon multi-protocol message broker is enabling you to build your data streaming network. Its exclusive algorithms enable you to do high-speed data streaming bidirectional.
The era of AI/ML are expired, and are now in the era of enabling high-speed internet for the next-generation digital transformation!
Article prepared by K. Thanansan, CEREXIO
